Polymer-Based Production of miRNA-Based Immune Modulators
miRNA regulation is complex in that a SINGLE miRNA can regulate 10-100's of genes and a SINGLE gene can be regulated by 10-100's of miRNA. Hence, the change of a SINGLE miRNA (up/down) is UNLIKELY to exert a potent systemic biological response due to the inherent complexity of miRNA expression, targeting and fidelity. Moreover, biological responses likely arise as a consequence of a PATTERN OF miRNA CHANGES that include unchanged, increased and decreased expression of MULTIPLE miRNAs. Thus, one must think of PATTERNS OF CHANGES. Our miRNA APPROACH has been to replicate the complex biologic miRNA patterns of change necessary to induce either a systemic pro-tolerogenic (TA1) or pro-inflammatory (IA1) state in the treated individual.
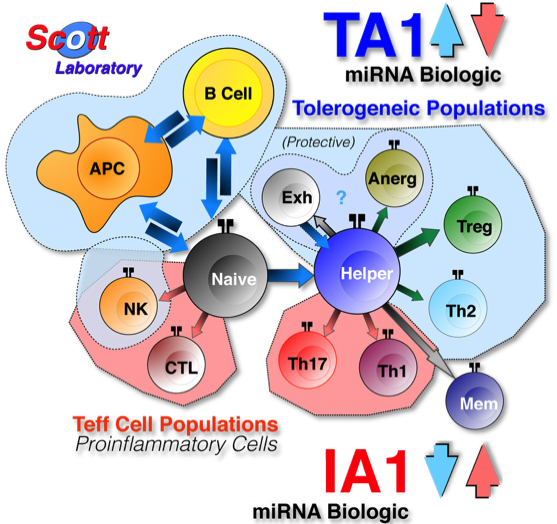
TA1: Tolerogenic miRNA therapeutic that induces an systemic immunoquiescent state inhibiting the onset or progression of autoimmune disease. May also improve transplantion outcome by inhibiting host-versus-graft disease (HVGD).
IA1: miRNA-based therapetuic that enhances the immune response to abnormal cells (e.g., cancer).
Our miRNA APPROACH has been to replicate the complex biologic miRNA patterns of change necessary to induce either a systemic pro-tolerogenic (TA1) or pro-inflammatory (IA1) state in the treated individual.
Development Pipeline
Wang, D., Shanina , I., Toyofuku, W.M., Horwitz, M.S. and Scott, M.D. Inhibition of Autoimmune Diabetes in NOD Mice by miRNA Therapy. PLoS ONE 10(12): e0145179. doi:10.1371/journal. pone.0145179 (2015).
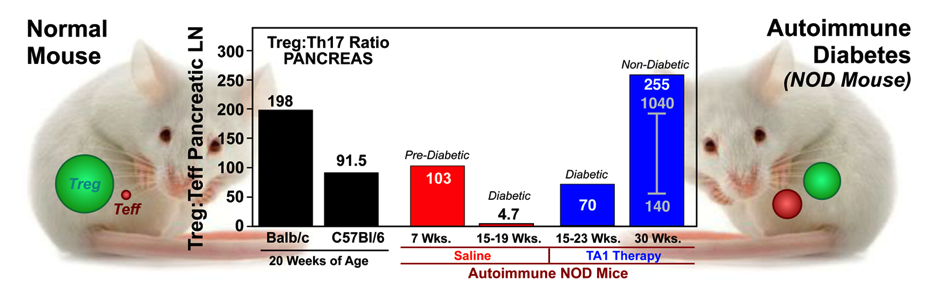

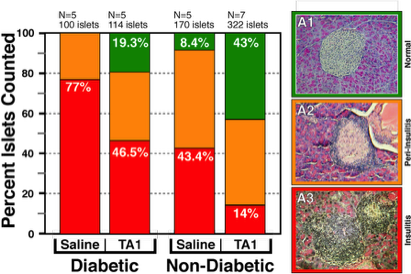
Autoimmune Type 1 Diabetes Reduced by TA1 Treatment
Pancreatic Islet Morphology is Significantly Improved in TA1 Treated Mice
TA Treatment INCREASES the ratio of T Regulatory (Treg) to T Effector (Teff; e.g., Th17) Lymphocytes
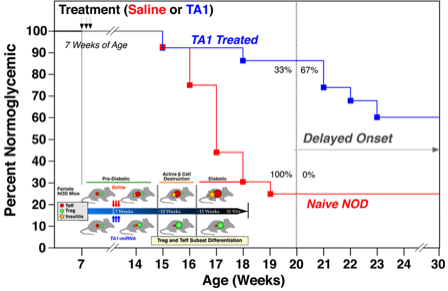
Utility of TA1 Therapy in Autoimmune (Diabetic) Mice
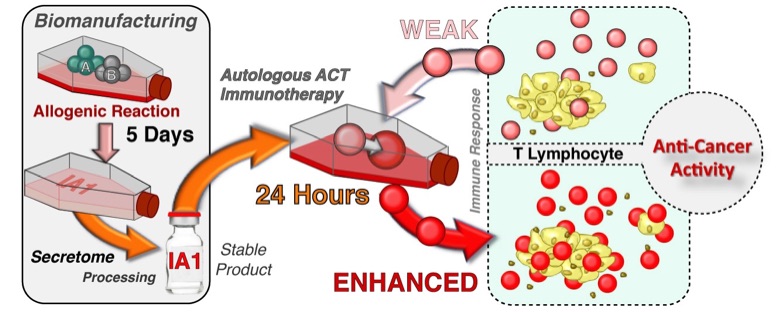
Utility of IA1 in Autologous Cancer Immunotherapy
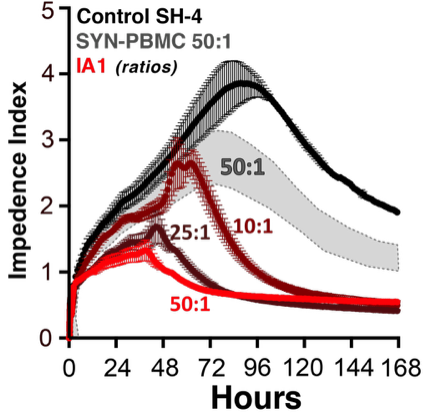
IA1 pretreatment of resting PBMC significantly inhibts SH-4 melanoma proliferation relative to the same PBMC without IA1 pretreatment (Grey shaded area; 50:1 ratio of PBMC to inital cancer cell count). Shown are the effects of IA1-activated PBMC (red lines) at ratios to SH-4 cells of 10:1, 25:1 and 50:1.
The bioproduction of IA1 is both inexpensive and rapid (5 days). The resultant product is stable during storage. Most importantly for patient care, ex vivo activation of autologous lymphocytes is rapid (24 hours).
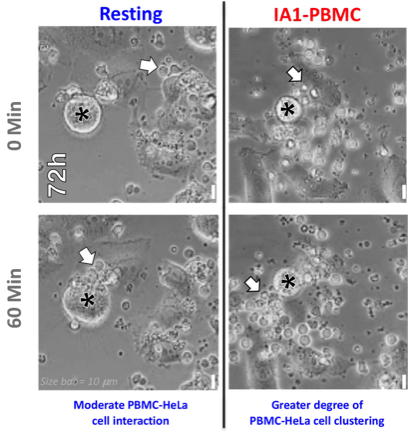
Microscopically IA1-pretreatment of PBMC resulted in increased recognition of cancer cells (*; HeLa cells) by human immune cells (white arrows). Cell:Cell interaction is crucial for immune cell killing of cancer cells.
Yang, X., Kang, N., Toyofuku, W.M., and Scott, M.D. Enhancing the Pro-Inflammatory Anti-Cancer T Cell Response Via Biomanufactured, Secretome-Based, Immunotherapeutics. Immunobiology, (2019). In press
Using bioreactor systems, the 'immunocamouflage' of leukocytes can be used to generate microRNA (miRNA) that can be administered in vitro or in vivo to induce either tolerance of a proinflammatory state. These miRNA biologics are stable and highly effective. the miRNA biologics modulate the immune system by regulating the Treg:Teff ratio.
Cancer Cell Proliferation