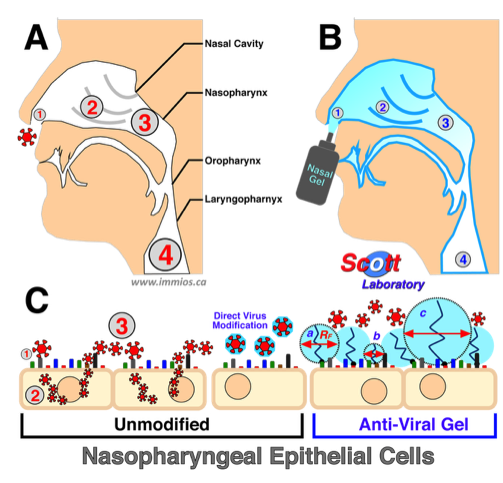
Broad Spectrum Antiviral Prophylactic Gel: The immunocamouflage technology has been successfully applied in the development of a broad spectrum anti-viral prophylactic gel. Our studies have documented the effectiveness of the anti-viral gel (e.g., suitable for intranasal administration) against a broad range of RNA and DNA, enveloped and non-enveloped, viruses. The prophylactic nasal gel is easy to apply and gives significant protection against viral invasion for at least 48 hours post application.
Canadian Blood Services manufactures and manages the blood supply for all Canadians. Created by Canada in 1998, it operates at arms length from the government of Canada.
Founded in 2002, the UBC Centre for Blood Research (CBR) applies emerging methods in biotechnology to the study of blood and blood processing in an integrated, interdisiplinary manner to create new knowledge in pursuit of health
Useful Links
Gel-Based Antiviral Prophylaxis
Blood Cell Deformability
Red Blood Cells, Iron & Oxidant Defense
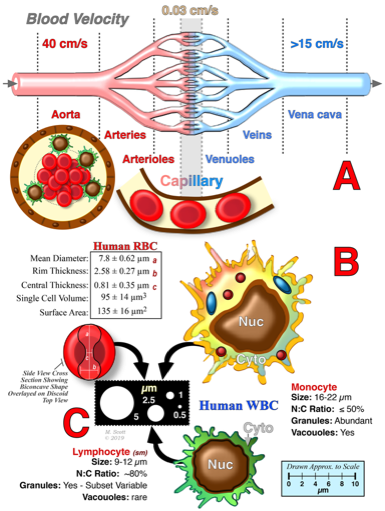
Among the most crucial rheological characteristics of blood cells within the vasculature is their ability to undergo the shape change (i.e., deform). The significance of cellular deformability is readily apparent based solely on the disparate mean size of human erythrocytes (~8 µm) and leukocytes (10-25 µm) compared to the minimum luminal size of capillaries (4-5 µm) and splenic interendothelial clefts (0.5-1.0 µm) they must transit. Over the past several years our laboratory has investigated the deformability of normal and abnormal blood cell using a variety of techniques (ektacytometry, micropore cell transit times and microfluidics). Most recently, we have been investigating how a new generation of small, inexpensive, microfluidic devices can be used to examine the vascular deformability of erythrocytes and leukocytes. These new microfluidic devices may prove useful in evaluating donor blood prior to transfusion and even in evaluating donors prior to blood collection.
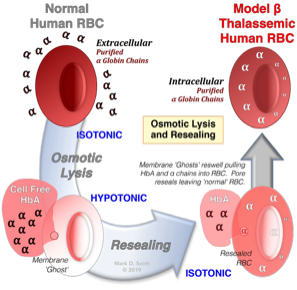
The Utility Of RBC Osmotic Lysis And Resealing For Studying Cellular Function And Dysfunction
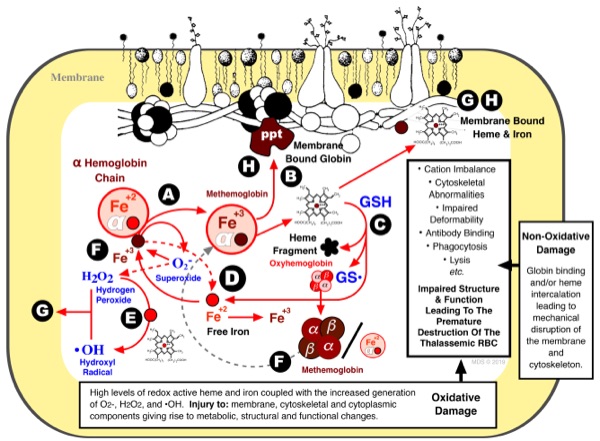
Unravelling the role of superoxide dismutase, catalase and GSH in the oxidant defense of human and mouse RBC.
Modeling human β thalassemic RBC to elucidate the mechanism(s) underlying the destruction of the thalassemic cell.
Jump to the Overview of:
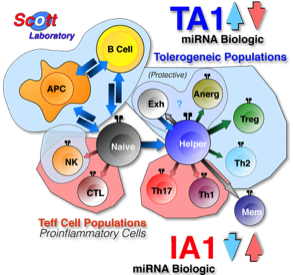
Using bioreactor systems, the 'immunocamouflage' of leukocytes can be used to generate microRNA (miRNA) that can be administered in vitro or in vivo to induce either tolerance of a proinflammatory state. These miRNA biologics are stable and highly effective. the miRNA biologics modulate the immune system by regulating the
Treg:Teff ratio.
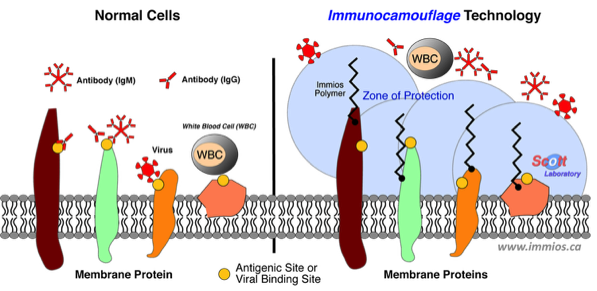
Over the last several years our laboratory has pioneered the development of the 'immunocamouflage' of foreign cells and tissues via cell surface modification with biocompatible polymers such as methoxypoly(ethylene glycol) [mPEG] and polyoxazolines [POZ]. The immunocamouflage of cells arises due to polymer obfuscation of the cell surface charge as well as the physical (steric) camouflage of antigenic epitopes by the highly mobile nanoscale grafted polymer structures. As a consequence, allorecognition of donor cell is dramatically attenuated. Our initial application of this 'stealth' technology has been in transfusion medicine (1996 - present) as a means of preventing RBC alloimmunization of the non-A/B blood groups.
Polymer- and miRNA-Based Immunomodulation


UBC




